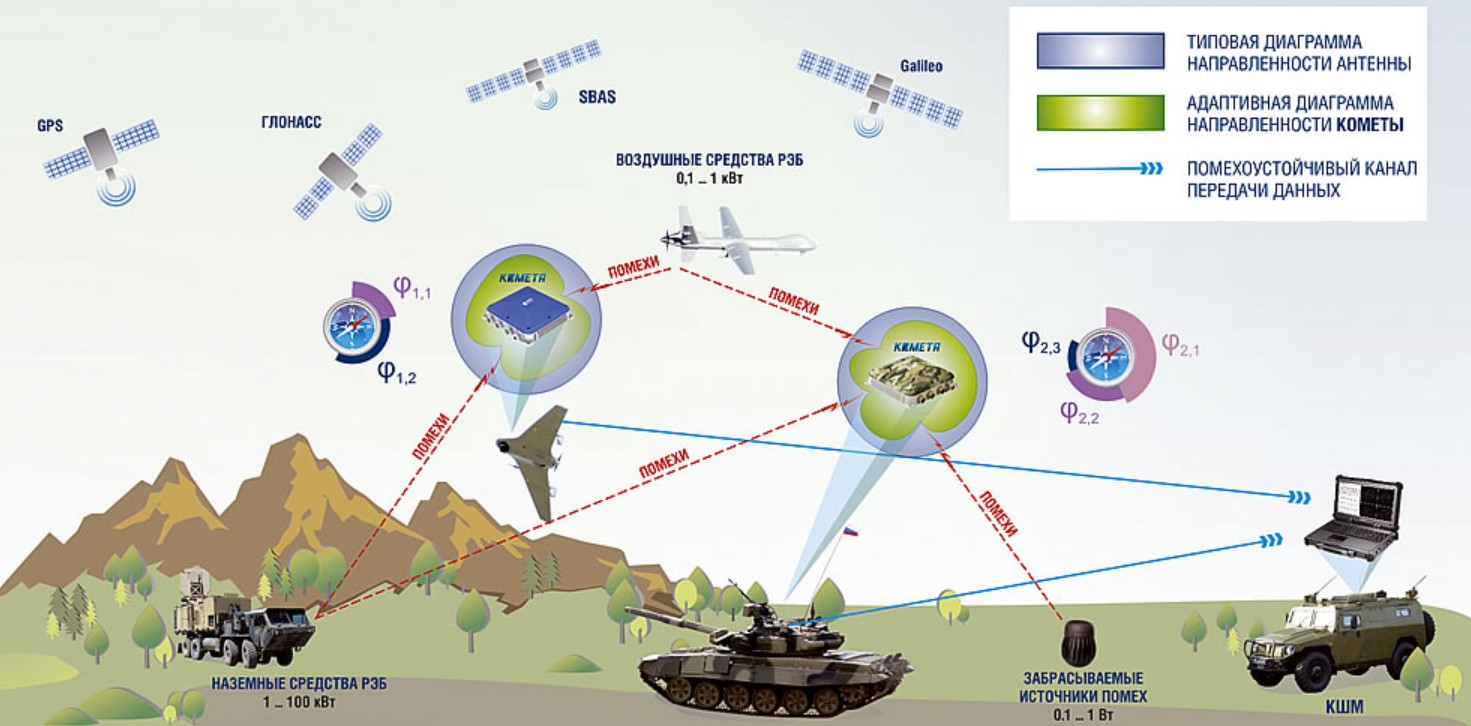
In modern warfare, it is unacceptable to use hardware unprotected from jamming on combat equipment.
For many years, Russia has been successfully engaged in developing a series of digital antenna arrays that should protect military equipment from jamming.
The developed Kometa device now greatly complicates the jamming operations of Ukrainian electronic warfare systems against drones.
Also, the Russians began to install the Kometa modules into gliding and correction kits for bombs, so that nothing prevented them from hitting the desired target.
GLONASS issue
With the development of technologies, receivers of global navigation satellite systems (GNSS) become more accessible, while their dimensions and weight decrease.
This suggests considering the possibility of installing GNSS receivers at various weapons, military and special equipment.
The presence of an accurate tool allows it to expand the capabilities of weapons, increasing the efficiency and improving the tactics.
Nevertheless, the Russian GLONASS radionavigation-satellite system for a long time was vulnerable to jamming.
GLONASS signals, like other satellite navigation systems, are easily susceptible to electronic suppression without special protection.
To remedy this situation, in 2008-2013, the development of jamming-resistant equipment was launched in Russia.
The prototype of the Kometa algorithm was first tested in 2007 on equipment weighing 40 kg. Already in 2012, JSC “VNIIR-PROGRESS” developed a new technology for creating digital antenna arrays, as a result of which weight and dimensions decreased with simultaneous improvement of functional characteristics.

Back in 2012, unlike the work of conventional receivers used in digital substations, the Kometa receiver during testing demonstrated confident reception of satellite signals even in conditions of interference that were tens of thousands of times higher than the threshold values of interference of conventional (unprotected) GLONASS/GPS receivers.
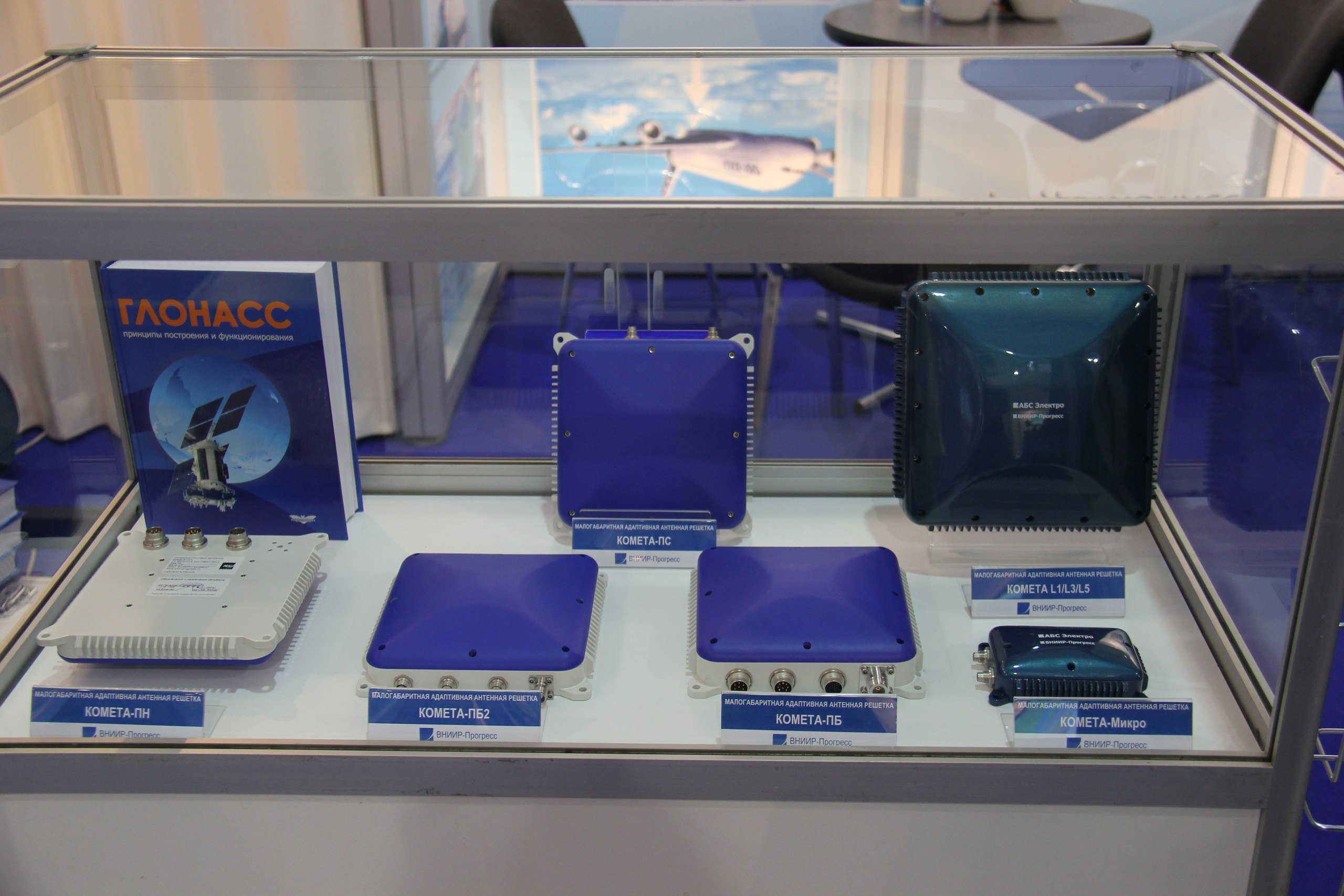
Thus appeared a series of “Kometa” receivers weighing less than 1 kg. Today, the mass of the most modern version is 60 g, which allows it to be used even on small drones.
Kometa vs EW
The receiver is designed to protect navigation signals from intentional and unintended interference to stabilize the signals of satellite navigation systems.
The “Kometa” series of digital antenna arrays is made in several design variants with many different versions:
- “Kometa-A” is designed for manned aviation;
- “Kometa-B” – for vehicles;
- “Kometa-N” – for terrestrial stationary objects;
- “Kometa-M” – for drones.
In the “Kometa” digital antenna arrays instead of one antenna element there are four, which allows it to obtain spatial information about the direction of arrival of the interference radiation and its compensation.
It is also worth noting that all elements of the “Kometa” are created in a single case.
The manufacturer claims that in a number of experiments it is shown that the “Kometa” withstands an interference level of 100,000 times greater than for a conventional receiver.
The drones that are equipped with this system are almost unaffected by electronic jamming systems.

“To “kill” the sixty-gram “Kometa,” the enemy will need two jamming systems, for 135-gram already five are needed , and seven or more – for individual products. Theoretically, it is difficult to deploy such a number of jamming systems on one site, in practice,” said the general director of the Russian enterprise.
Four-element small-size adaptive antenna arrays provide protection for GNSS navigation signals of the L1 range (GLONASS, GPS, Galileo, SBAS) with open access (Open Service).
The antennas of this series increase resistance to interference by 40-50 dB, which is equivalent to a decrease in the suppression radius by 100-300 times.
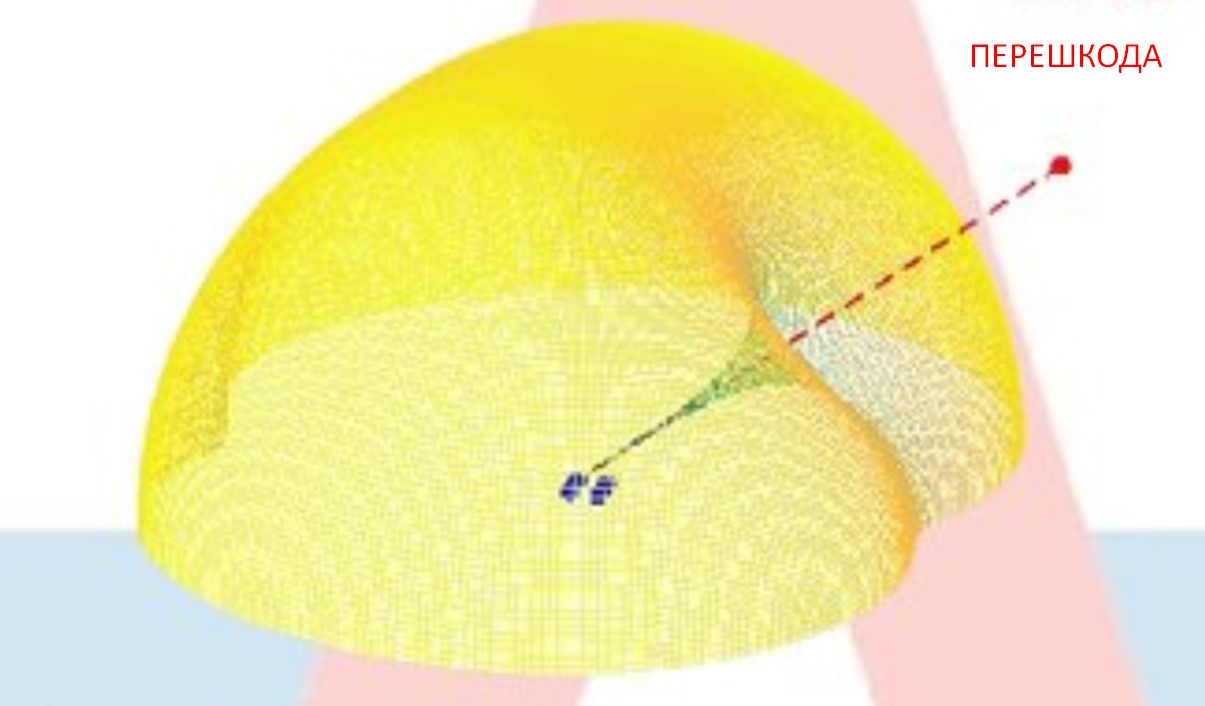
The main results of the first tests showed that the “Kometa” provides an increase in noise immunity to 32… 56 dB, providing a level of noise immunity J/S = 92… 108 dB when exposed to three broadband/narrowband interference.
Characteristics of “Kometa” weighing 1 kg are as follows:
- Weight 1.0 kg
- Dimensions 172 *172 *42 mm
- Number of antenna elements 4
- Operating temperature -40 to + 60 °C
- Power consumption 12 W
- Number of channels 32
- Supported signals GPS/GALILEO/SBAS-L1 1575/42 MHz/ ГЛОНАСС-L1 1597.5, 1609.5 MHz
- Protected navigation signal range GNSS-1593, 1610.5 MHz (GLONASS L1): 1573, 1578 MHz (GPS L1, Galileo E1, SBAS L1)
- 40-50 dB broadband jamming
- Noise immunity, J/S 90 dB
- Physical interface RS422/RS485, PPS, HF output
- NMEA Data Exchange Protocol (default), BINR
- Digital information coordinate-time storage and navigation information, interference assessment, diagnostic

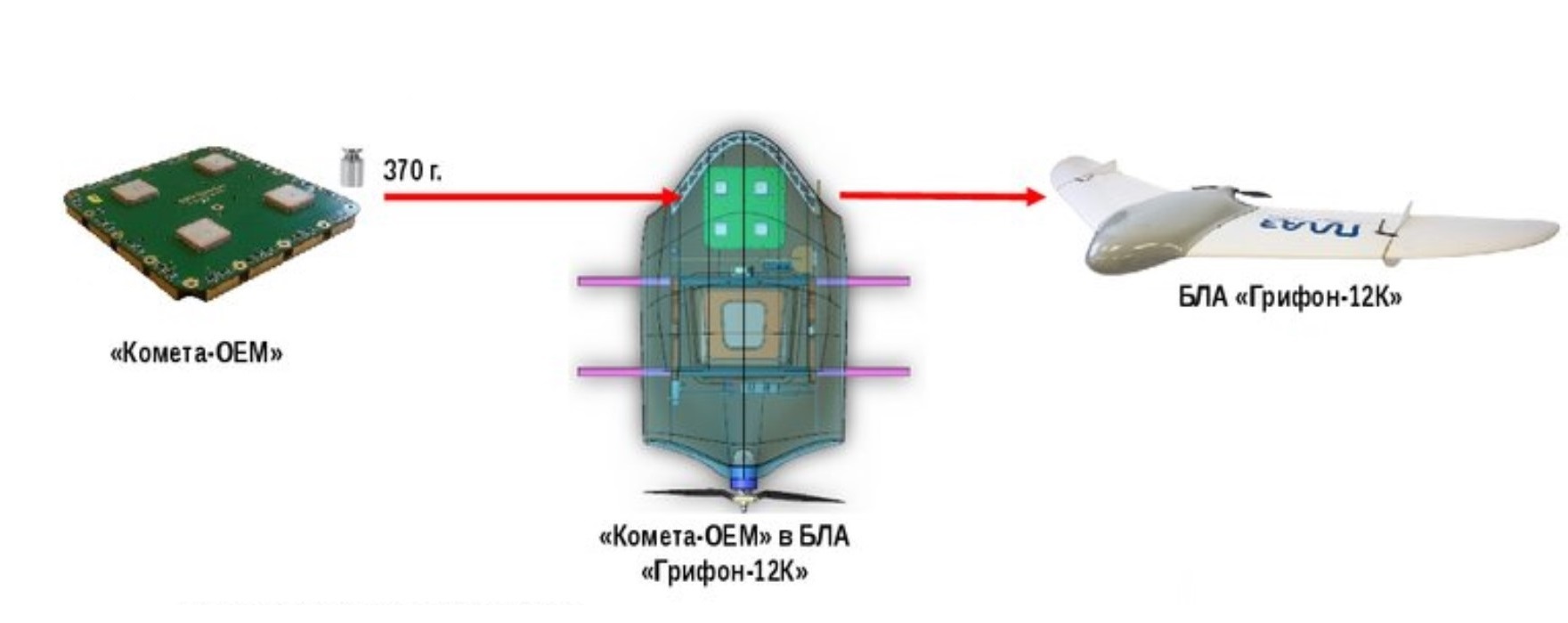
Let us also look at the option for drones – “Kometa-OEM”.
In “Kometa-OEM”, the antenna is used in the range of GNSS navigation signals with open access L1 and provides simultaneous operation of 3 channels.
The antennas of the “Kometa” type with a power of 12 W (+ 15%) operate from a DC power supply of 8-52 V.
They are shock-resistant, have dust-resistant (IP20) climatic (В5.1) design and work steadily at changes in external temperatures.
They also differ in small dimensions (152*152*15 mm) and their weight does not exceed 0.37 kg.
Use in Ukraine
In Ukraine, the Russian military began to use the latest version of the “Kometa-M” for drones and gilded bombs to protect them from jamming of satellite communications.

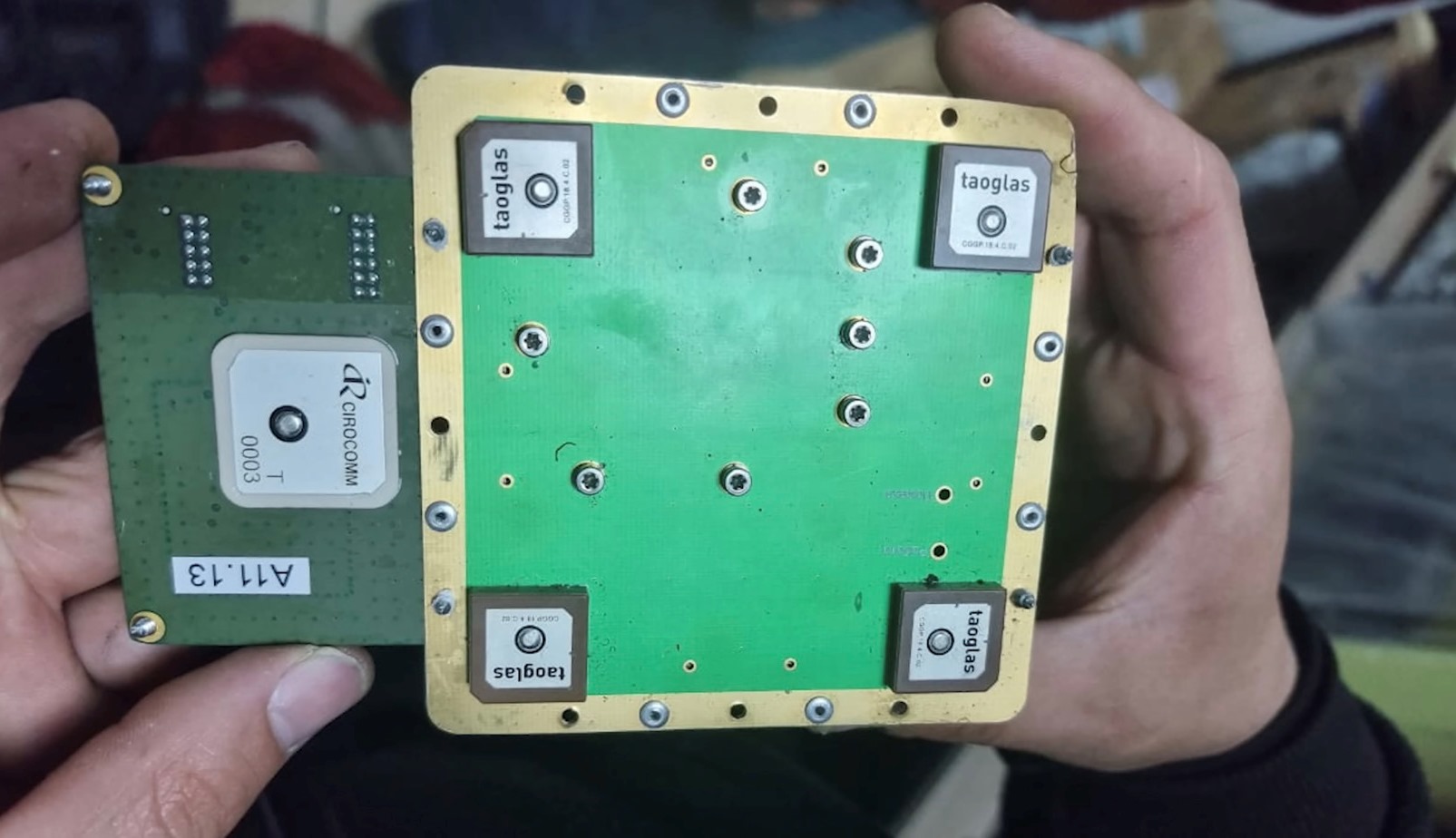
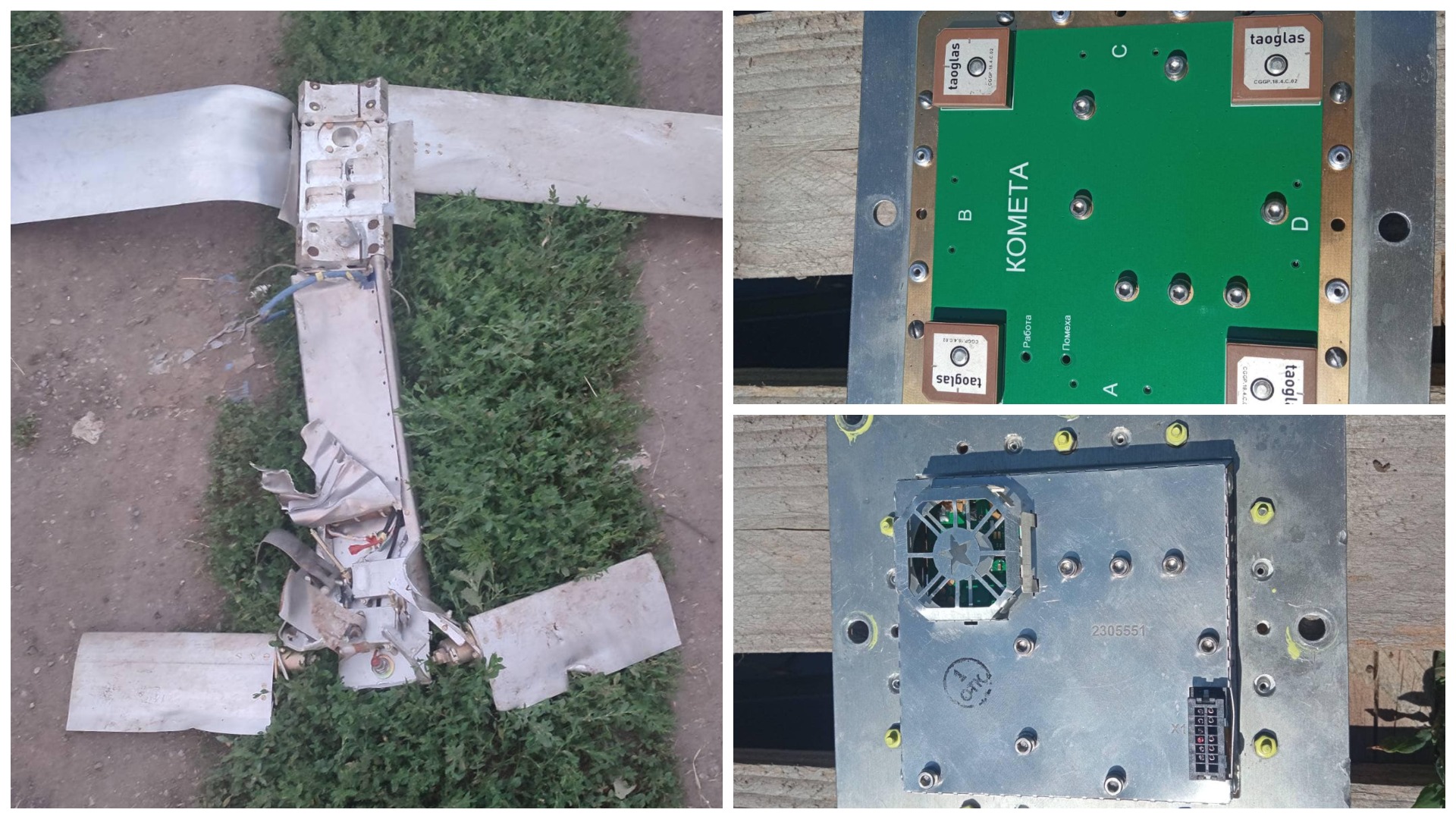
Initially, the Orlan-10 reconnaissance drone fell into the hands of the Ukrainian military, in which the 2022 “Kometa-M” was discovered.
This “Kometa” uses components from American companies Altera/Intel, Taoglas and Taiwan’s Cirocomm. The new “Kometa-M” already has a size of 100*100*30 mm and weighs 150 grams.
The Russians would not be able to fully use their Orlan-10 reconnaissance drones without these digital antenna arrays. They would immediately fall under the influence of electronic warfare systems of Ukraine.
In 2023, the Russians begin to drop bombs on Ukrainian positions, which are equipped with a gliding and correction module and make bombs more accurate with an increased range.
At these modules, the Russian defense-industrial complex also began to install “Kometa-M” small-sized adaptive antenna arrays.
“Kometa-M” on gravity bomb modules should significantly complicate the work of Ukrainian electronic warfare systems, which will try to jam and knock off the course of the gliding and correction module so that the bomb does not hit its target.
To complicate the use of “Kometa,” the Ukrainian military needs to get more electronic warfare systems.
Also, allies of Ukraine can make greater efforts and block the supply channels of Western components to these digital antenna arrays.
SUPPORT MILITARNYI
Even a single donation or a $1 subscription will help us contnue working and developing. Fund independent military media and have access to credible information.


 Роман Приходько
Роман Приходько 
 Віктор Шолудько
Віктор Шолудько 
 Андрій Харук
Андрій Харук 

 Андрій Тарасенко
Андрій Тарасенко 
 Yann
Yann 
 СПЖ "Водограй"
СПЖ "Водограй" 

 ГО "Військова школа "Боривітер"
ГО "Військова школа "Боривітер" 

 Катерина Шимкевич
Катерина Шимкевич 
 Олександр Солонько
Олександр Солонько 
 Андрій Риженко
Андрій Риженко 


